Shock Loss After a Hair Surgery: Is It Normal?
Hair loss is a common concern for many people. Following a hair transplant, patients may be surprised to find that they are experiencing hair loss as a side effect. There are two primary types of post-surgical hair loss: shedding and shock loss.
In this article, we will explore the causes of hair loss after a hair transplant, discuss whether this loss is temporary, and offer practical advice on how to manage and prevent it.
The Role of Anaesthesia in Shock Loss
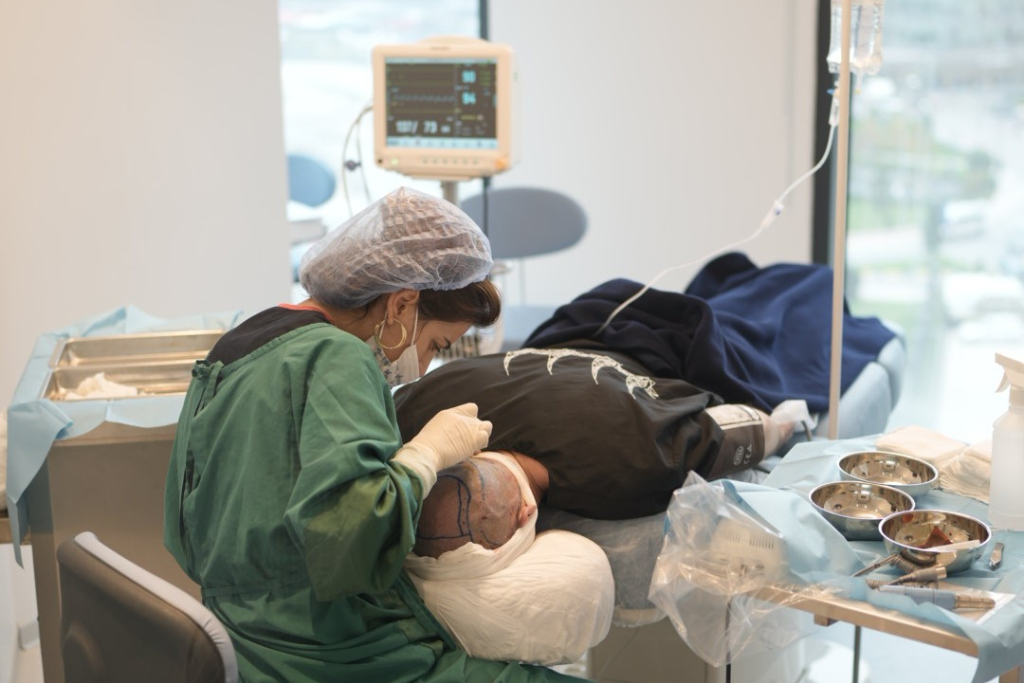
At Elithair, every hair transplant begins with our Sleep Deep method, followed by local anaesthesia to ensure maximum comfort. However, the anaesthetic process, combined with the surgery, can be perceived as a stressor by the body. This can disrupt the body’s natural balance, known as homeostasis, temporarily disrupting the nervous system and causing the body to produce higher levels of cortisol.
Increased levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can constrict blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the scalp. As a result, hair follicles may lack essential nutrients, causing hair growth to slow down or stop altogether. This process leads to what is called “shock loss”.
Other Factors Contibuting to Shock Loss
While anaesthesia is a significant trigger, other factors may also lead to shock loss. It’s a complex biological process which can involve pre-existing conditions. Chronic illnesses such as diabetes and thyroid dysfunction can contribute to hormonal imbalances, which can further impact your hair’s natural growth cycle.
Diet and Medication
Hair needs nutrients to stay healthy. A diet that is too restrictive can deprive hair of the nutrients it needs. Lack of protein, vitamins, and minerals can weaken your hair and lead to hair loss. Without the nutrients they need, follicles can stop producing new hair, leading to temporary hair loss.
Blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and anti-depressants can also cause hair loss. If you are taking medication and notice that you are experiencing hair loss as a side effect, talk to your doctor to find a solution.
What is the Difference Between Shedding and Shock Loss?
Post-Surgical Shedding
Shedding typically begins 2–3 weeks after the transplant, but can happen at any time within the first 2-3 months post-surgery. This occurs as transplanted hair enters the resting (telogen) phase. This is a normal and temporary process that indicates the beginning of a new growth cycle.
This type of hair loss is known as “telogen effluvium” and can last for up to 6 months. The hair is shed as part of the normal, healthy growth cycle, allowing the newly transplated grafts to produce regrowth. This is known as the anagen phase.
Hair growth usually resumes within 3–4 months, with full results visible in 12–18 months.
Shock Loss
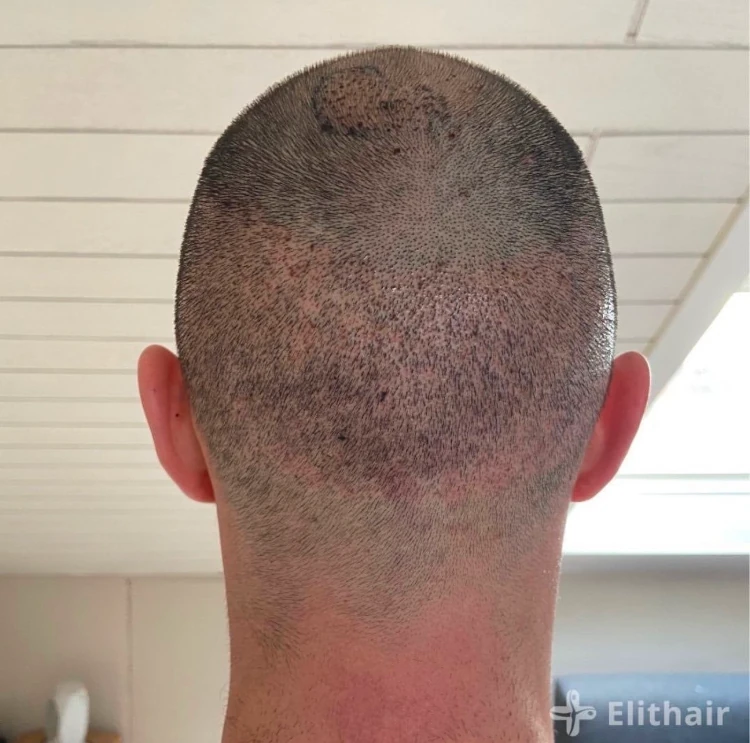
Shock loss, on the other hand, can occur shortly after the transplant. Unlike shedding, shock loss may affect existing hair near the transplant site. If excessive follicles are extracted or if the body reacts strongly to stress, higher volumes of cortisol are produced in the body.
Each hair follicle has its own adrenal gland from which cortisol is secreted. The cortisol released by these glands can cause hair to fall out. The shock can be immediate or can occur a few days after the operation, leading to hair loss. As a result, the surrounding donor or transplanted areas may show thinning or bald patches.
Unlike shedding, shock loss can negatively effect the final results of your transplant, as grafts can be rejected by the body and the donor area might not grow back properly. If this occurs, it is essential to consult your clinic.
Reversing Hair Loss After Surgery

While shock loss can be concerning, it is often reversible. Here are some steps to promote recovery:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in iron, biotin, and essential fatty acids can strengthen hair. Include foods like spinach, eggs, and avocados in your meals.
- Activities like walking, yoga, or spending time in nature can lower cortisol levels, improving overall well-being and hair health.
- Avoid tight hairstyles and use mild, nourishing hair products.
- Consider using doctor-recommended treatments like minoxidil or PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy to stimulate hair regrowth.
Have you tried the Elithair hair care range?
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Balwi, the Elithair hair care range is concentrated in essential natural nutrients such as biotin . Unlike those available commercially, our hair care products nourish your hair directly from its roots. Don’t wait any longer to give your hair new vitality!
Your Path to Stronger Hair
Shock loss is a rare and temporary side effect of hair transplantation. With proper care and expert guidance, your hair will recover, leaving you with thicker, healthier locks. If you have concerns, don’t hesitate to consult your clinic.
Are you ready to take the next step toward restoring your hair? Start with a free hair analysis today and explore affordable, world-class hair transplants in Turkey with Elithair.
FAQ
What causes shedding and shock loss?
Shedding is caused by telogen effluvium, where hair enters the resting phase prematurely. Shock loss occurs due to follicle trauma, often linked to anaesthesia or over-extraction.
How long does shedding last after a hair transplant?
Shedding typically lasts 2–3 months and may continue for up to 6 months.
How common is shock loss?
Shock loss is relatively rare and depends on the surgical technique and individual patient response.
Can shedding and shock loss be treated?
Yes. Treatments such as minoxidil, PRP therapy, and proper hair care can help minimise these effects.
How can I tell the difference between shedding and shock loss?
Shedding results in diffuse hair loss, while shock loss often causes patchy bald spots or thinning.
Does shock loss affect transplant results?
Shock loss may impact final results if the transplanted follicles fail to survive or if the donor area experiences significant thinning.
What role does stress play in hair loss?
Stress elevates cortisol levels, which can disrupt blood flow and nutrient supply to hair follicles, leading to shedding or shock loss.
What are the signs of recovery after a shock loss episode?
Recovery signs include reduced shedding, new hair growth in affected areas, and improved density over time.
Can certain patients be more prone to shock loss or shedding?
Yes, factors like genetics, health conditions, and the surgical technique used can influence susceptibility.
How can I prevent post-operative shock loss?
Avoiding tight hairstyles, using gentle hair products, following a balanced diet, and reducing stress are key to preventing shock loss.