Understanding Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Scalp and hair follicle infections can cause significant discomfort and lead to hair loss if not properly treated. These infections are often caused by bacteria, fungus, or viruses and can be present with a variety of symptoms. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for scalp and hair follicle infections is essential for maintaining healthy hair and scalp. This comprehensive article will provide insights into these conditions and offer guidance on prevention and management.
Table of Contents
- Causes of Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
- Symptoms of Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
- Diagnosing Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
- Treatment Options for Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
- Scalp infections and hair transplants
- Preventing Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
- Conclusion
Causes of Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
The following is a summary of the main bacterial, fungal, viral and other infections of the scalp.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections of the scalp and hair follicles are frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium can enter the skin through cuts, abrasions, or insect bites, leading to infections such as folliculitis or cellulitis.
- Folliculitis: This common condition involves the inflammation of hair follicles, typically due to bacterial infection. It appears as red, swollen bumps that may be itchy or painful.
- Cellulitis: This is a more severe bacterial infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and can spread quickly. It causes redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections of the scalp are typically caused by dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments. The most common fungal infections include:
- Tinea Capitis: Also known as ringworm of the scalp, this infection is caused by a fungus that invades the hair shafts and scalp. It leads to scaly, itchy patches and hair loss.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This chronic condition is characterised by greasy, yellowish scales and red, inflamed skin. It is often associated with an overgrowth of the yeast Malassezia.
Viral Infections
Viral infections can also impact the scalp and hair follicles, though they are less common. Conditions such as shingles can lead to painful, blistering rashes on the scalp. These are some of the most frequent:
- Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) or shingles: Infection with this virus appears as painful rashes anywhere on the body, including the scalp. It can cause discoloured patches on the skin of the scalp with bumps or blisters that eventually crust over.
- Human papilloma virus (HPV): Scalp warts are caused by HPV and are a particular risk for men who receive frequent back-to-back haircuts that require firm pressure to ensure uniform length.
Other Scalp Infections
Some scalp infections are caused by parasites, have an autoimmune origin or an unknown cause. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Pediculosis capitis: This condition produces an infestation of the hairy parts of the body with lice eggs or larvae (nits) or adult lice. The larval stages of this insect feed on human blood, causing severe itching.
- Psoriasis: This skin disease causes rashes with red, scaly, itchy patches, especially on the knees, elbows, trunk and scalp.
Symptoms of Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
The symptoms of scalp and hair follicle infections vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. These are some of the symptoms that indicate a possible scalp infection:
- Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas may become red, swollen, and tender to the touch.
- Itching and Discomfort: Itching is a common symptom of both bacterial and fungal infections.
- Hair Loss: Infections can damage hair follicles, leading to temporary or permanent hair loss in the affected areas.
- Scaly Patches: Fungal infections regularly cause scaly, flaky patches on the scalp.
- Pustules and Blisters: Bacterial infections like folliculitis can result in pustules (pus-filled bumps) or blisters.
- Pain: Viral infections such as shingles can cause significant pain and discomfort.
Diagnosing Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
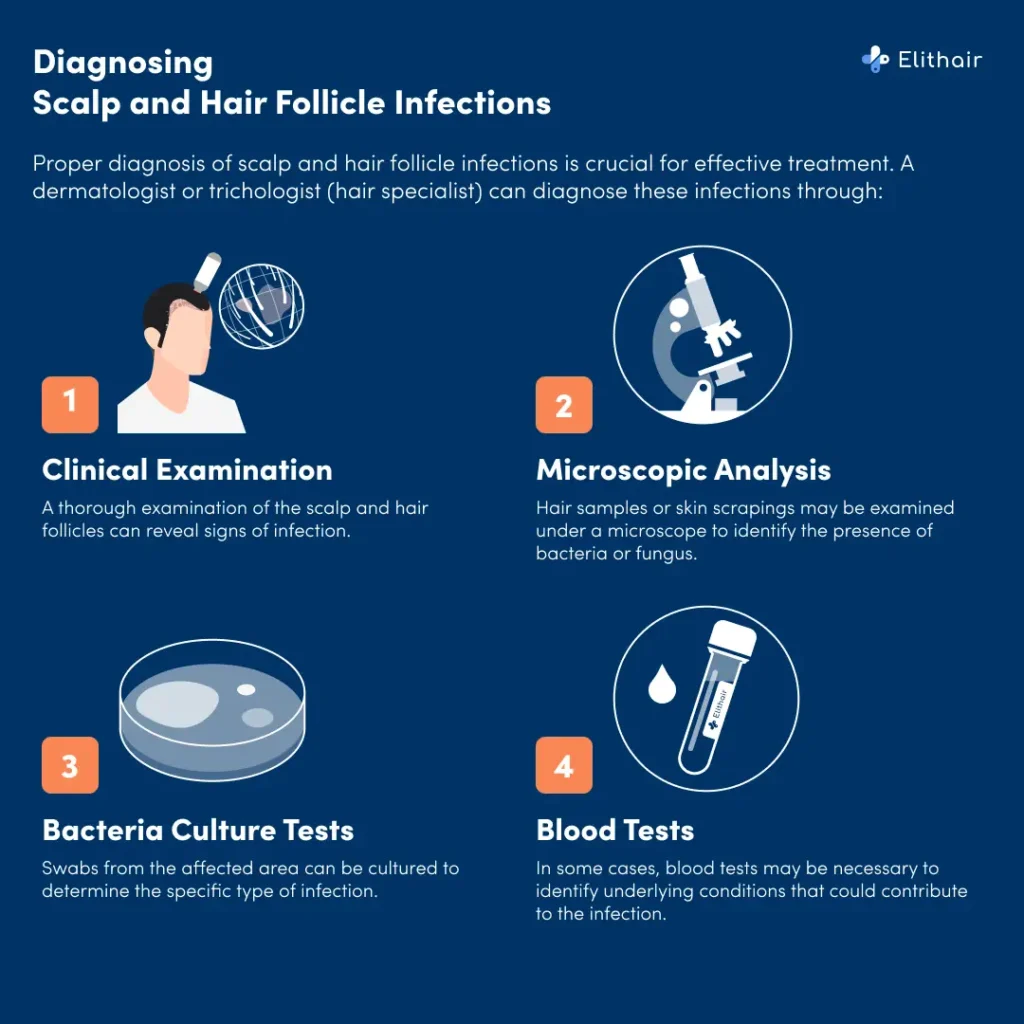
Proper diagnosis of scalp and hair follicle infections is crucial for effective treatment. A dermatologist or trichologist (hair specialist) can diagnose these infections through:
- Clinical Examination: A thorough examination of the scalp and hair follicles can reveal signs of infection.
- Microscopic Analysis: Hair samples or skin scrapings may be examined under a microscope to identify the presence of bacteria or fungus.
- Culture Tests: Swabs from the affected area can be cultured to determine the specific type of infection.
- Blood Tests: In some cases, blood tests may be necessary to identify underlying conditions that could contribute to the infection.
Treatment Options for Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections
Treatment for scalp and hair follicle infections depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common treatment options include:
Antibacterial Treatments
- Topical Antibiotics: Creams or ointments containing antibiotics can be applied directly to the affected area to treat bacterial infections.
- Oral Antibiotics: For more severe bacterial infections, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection from within.
Antifungal Treatments
- Antifungal Shampoos: Medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole or selenium sulphide can help treat fungal infections like tinea capitis.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: For persistent or severe fungal infections, oral antifungal medications may be necessary.
Antiviral Treatments
- Antiviral Medications: Conditions like shingles can be treated with antiviral medications to reduce symptoms and speed up recovery.
- Pain Relief: Pain management may include over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications.
Supportive Treatments
- Steroid Creams: Topical steroids can reduce inflammation and itching associated with infections.
- Moisturisers and Emollients: Keeping the scalp moisturised can help manage symptoms and promote healing.
Scalp infections and hair transplants
Hair health can be compromised by various scalp infections, leading to temporary or permanent hair loss. The table below is a key reference for understanding how various scalp infections can lead to hair loss, aiding both patients and healthcare providers in determining the best course of treatment, including hair transplant options.
Scalp infections can be caused by bacteria, fungus, or viruses, and each has specific symptoms and treatments. Some infections, if not treated promptly, can cause permanent damage to hair follicles, resulting in irreversible hair loss.
Although many of these scalp infections are not compatible with a hair transplant while they are active, once treated, it may be possible. Therefore, it is important to see a trichologist or dermatologist to get the most effective treatment and have a hair analysis before knowing if it is possible to undergo a hair transplant.
| Scalp Infection | Causes Hair Loss | Suitable for Hair Transplant |
| Folliculitis | ✔ | X |
| Cellulitis | ✔ | X |
| Tinea Capitis | ✔ | X |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | ✔* | X |
| Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) | ✔** | X |
| Human papilloma virus (HPV) | X | X |
| Pediculosis capitis | X | X |
| Psoriasis | ✔*** | ✔**** |
* Although Seborrheic Dermatitis does not cause hair loss directly, severe dandruff can cause a person to scratch the scalp so hard that it injures the scalp.
** Even though it does not cause hair loss directly, it can cause hair loss when combing or scratching.
*** Scalp psoriasis itself does not cause hair loss. However, excessive scratching, aggressive treatments and the stress associated with the condition can cause temporary hair loss.
**** According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery: “Hair transplantation can be performed in patients with psoriasis, with prior warning of the possibility of Koebner’s phenomenon. Even if it does occur, it will not negatively affect the result of the hair transplant if adequate dermatological treatment is provided.”
Preventing Scalp and Hair Follicle Infections

By adopting these preventive measures, you will significantly reduce the risk of developing scalp and hair follicle infections. If you experience persistent or unusual symptoms, consult a dermatologist for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
- Maintain good hair hygiene
- Washing frequency: Determine the right washing frequency for your hair type. Washing too often can dry out the scalp, while insufficient washing can promote bacterial growth.
- Shampoo choice: Choose a gentle, sulphate-free shampoo that respects the natural balance of the scalp. Avoid harsh products that can irritate the skin.
- Thorough rinsing: Make sure to rinse your hair thoroughly after shampooing to remove any product residue.
- Gentle drying: Avoid rubbing your hair vigorously with a towel. Instead, gently pat it to absorb excess water.
- Prevent the transmission of infections
- Personal hygiene: In addition to combs, brushes, hats, and pillows, avoid sharing other personal items that may come into contact with your scalp, such as scarves or headphones.
- Tool disinfection: Regularly clean your hair tools with a disinfectant product.
- Hair salons: Ensure that hair salons follow hygiene standards and use sterilised equipment.
- Keep the scalp dry
- Drying after showering: Thoroughly dry your scalp after showering, especially in folded areas.
- Sweating: Regularly change your hat or protective helmet when you sweat heavily.
- Humid conditions: Avoid staying in humid environments, such as pools or saunas, for extended periods.
- Protect the scalp
- Sun exposure: Wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect your scalp from harmful UV rays, which can cause premature ageing and certain skin conditions.
- Hair products: Use hair products that contain sunscreen for added protection.
- Injuries: Avoid scratching or touching your scalp to prevent infections.
- Manage stress
- Relaxation techniques: Regularly practise relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Physical activity: Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Sufficient sleep: Ensure you get enough sleep to allow your body to regenerate and strengthen your immune system.
Conclusion
Scalp and hair follicle infections can cause significant discomfort and affect your hair’s health and appearance. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effectively managing these conditions. If you suspect you have a scalp or hair follicle infection, consulting a dermatologist or hair specialist can provide you with an accurate diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan. By maintaining good hygiene, taking preventative measures, and seeking professional help when needed, you can ensure a healthy scalp and beautiful hair.
FAQ
Can a scalp infection cause permanent hair loss?
Yes, untreated scalp infections, particularly fungal and bacterial ones, can lead to permanent hair loss due to damage to the hair follicles. Early treatment is key to preventing long-term effects.
Are scalp infections contagious?
Some scalp infections, such as fungal infections like ringworm, are highly contagious, while others like bacterial infections are generally not. Proper hygiene can help reduce the spread.
Can stress trigger scalp infections?
While stress itself doesn’t cause infections, it can weaken the immune system, making the scalp more vulnerable to bacterial or fungal overgrowth, which can lead to infections.
How can I prevent future scalp infections?
Maintaining good scalp hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items like combs, and addressing any scalp irritations promptly can help prevent infections. A healthy diet and lifestyle also support scalp health.
Can a scalp infection affect the overall health of my hair?
Yes, scalp infections can lead to hair thinning or even hair loss if left untreated. The health of your scalp is directly related to the health of your hair.