Olumiant: Hair Loss Drug for Alopecia Areata Treatment Approved In UK
Alopecia Areata is a health condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. It is an autoimmune disorder for which there is currently no cure. However, it is possible to treat the symptoms of Alopecia Areata. Oluminant is a medication which has been approved by both the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in the United Kingdom.
In this article, we’ll be taking a closer look at alopecia areata, how Oluminant works, and who might benefit from taking this hair loss medication.
Summary
- A Brief Overview of Alopecia
- How Does Olumiant Work?
- Overview of the Clinical Studies on Olumiant for Alopecia
- Safety and Side Effects
- Olumiant for Alopecia vs. Other Conditions
- What Is the Current Availability of Olumiant for Alopecia?
- Conclusion
A Brief Overview of Alopecia
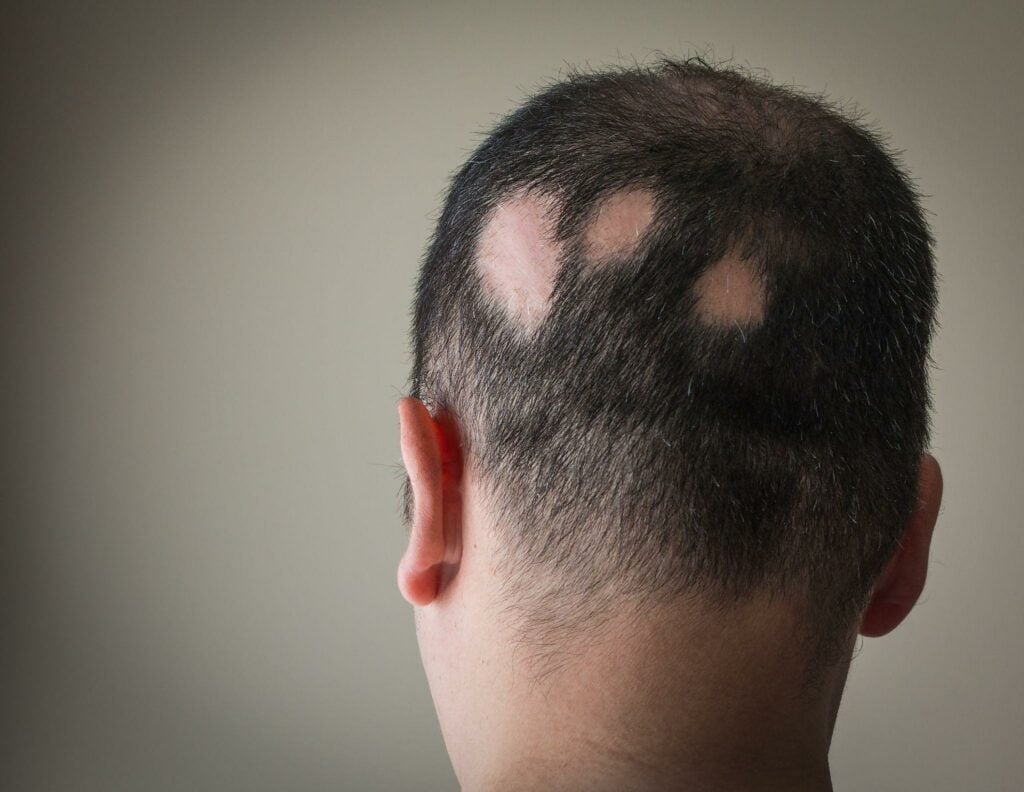

Alopecia is a medical condition characterised by hair loss, which can occur on the scalp or other parts of the body. It can be temporary or permanent and may result from various factors, including genetics, autoimmune disorders, hormonal changes, stress, or certain medical treatments like chemotherapy.
Alopecia areata specifically refers to a type of hair loss where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to sudden and often patchy baldness. This condition can have significant emotional and psychological impacts, affecting self-esteem and quality of life.
The most common treatment options include medications, topical treatments, injections, and, in some cases, hair transplantation.
How Does Olumiant Work?
Olumiant, also known as baricitinib, is a medication classified as a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. It works by targeting specific enzymes called JAKs, which play a crucial role in the signalling pathways involved in inflammation and immune responses. By inhibiting these enzymes, Olumiant helps to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, making it useful in treating autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis.
In cases of alopecia, JAK inhibitors like Olumiant have garnered attention for their potential therapeutic effects. As alopecia areata, in particular, is believed to involve an autoimmune attack on hair follicles, JAK inhibitors may help by interfering with the immune response that targets these follicles, potentially allowing hair to regrow.
Clinical trials investigating the use of JAK inhibitors, including Olumiant, for alopecia areata have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing significant hair regrowth.
Overview of the Clinical Studies on Olumiant for Alopecia
Clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of Olumiant specifically for different types of alopecia are still relatively limited compared to other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. However, there have been some investigations into its potential use for alopecia areata, alopecia barbae (facial hair loss), and traction alopecia. Here’s an overview:
Alopecia Areata: Several small-scale studies and case reports have explored the use of JAK inhibitors, including Olumiant, for alopecia areata. These studies have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing significant hair regrowth. For example, one study showed that patients treated with Barticinib for hair regrowth had regained at least 80% of their lost hair after 36 weeks.
Alopecia Barbae: Alopecia barbae, characterised by hair loss in the beard area, shares similarities with alopecia areata in terms of its autoimmune nature. While there is limited specific research on Olumiant for alopecia barbae, the findings from studies on alopecia areata suggest that JAK inhibitors could potentially be effective for this condition as well.
Traction: Traction alopecia is caused by repetitive pulling or tension on the hair follicles, often due to hairstyles like tight braids or ponytails. Unlike alopecia areata, traction alopecia is not autoimmune in nature. While JAK inhibitors like Olumiant target immune-mediated hair loss, they may not be effective for traction alopecia. Treatment for traction alopecia typically involves avoiding hairstyles that cause tension on the hair follicles and promoting healthy hair care practices.
Safety and Side Effects
The safety and side effects of Olumiant, specifically for alopecia areata, are not fully established due to limited dedicated clinical studies. However, based on its use in other conditions, potential side effects may include an increased risk of infections, gastrointestinal issues, headaches, and changes in liver enzymes.
As with any medication, individual responses can vary, and close monitoring is crucial. That said, given the autoimmune nature of alopecia areata, ongoing research is needed to comprehensively assess the safety and effectiveness of Olumiant for this specific type of hair loss.
Olumiant for Alopecia vs. Other Conditions
Olumiant presents a potential therapeutic avenue for various autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and atopic dermatitis (AD). Olumiant’s ability to inhibit Janus kinase pathways helps mitigate inflammation and joint damage, making it a valuable option for individuals with moderate to severe RA who haven’t responded well to conventional treatments.
In AD, Olumiant’s immunomodulatory effects have shown effectiveness in reducing skin inflammation and symptoms associated with AD, particularly in cases resistant to other therapies.
However, while Olumiant offers therapeutic potential across these conditions, its use requires careful consideration due to the potential side effects, including an increased risk of infections and other adverse reactions (as discussed above). Moreover, its long-term safety profile and optimal dosing regimens also need further evaluation.
What Is the Current Availability of Olumiant for Alopecia
The UK’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) granted marketing authorisation for Olumiant for the treatment of alopecia areata in October 2022. However, Olumiant was not recommended by NICE for routine commissioning in the NHS and can only be obtained with a private prescription. Treatment must be started by a specialist who has experience in the diagnosis and treatment of alopecia areata.
Conclusion
While JAK inhibitors like Olumiant show promise in addressing autoimmune-related hair loss, including alopecia areata, their efficacy and safety profiles are still being evaluated. Currently, hair transplantation stands as one of the most effective treatments for hair loss, offering more predictable and long-lasting results.
At Elithair, we offer exceptional results for hair loss through advanced hair transplant techniques, providing natural-looking and permanent solutions for patients. Contact us today to book a free consultation.
FAQ
How does Olumiant compare to other hair loss treatments in terms of effectiveness?
Olumiant has shown promising results for treating alopecia areata, with some patients experiencing significant hair regrowth. However, its effectiveness compared to other treatments like minoxidil or finasteride varies, and it may not be suitable for all types of hair loss.
Are there any contraindications for using Olumiant for hair loss?
Contraindications for using Olumiant include existing infections, a history of blood clots, liver disease, or certain cancers. Patients should consult their healthcare provider to ensure it is safe based on their medical history.
Can Olumiant be used in combination with other hair loss treatments?
Olumiant can sometimes be used alongside other treatments like topical minoxidil or PRP therapy, but this should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions and side effects.
Can Olumiant be used to treat other types of alopecia apart from alopecia areata?
While Olumiant is primarily approved for alopecia areata, there is ongoing research into its effectiveness for other types of alopecia, such as androgenetic alopecia and traction alopecia. Its use for these conditions is not yet fully established.
What lifestyle changes can support the effectiveness of Olumiant in treating hair loss?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can support the effectiveness of Olumiant in treating hair loss.