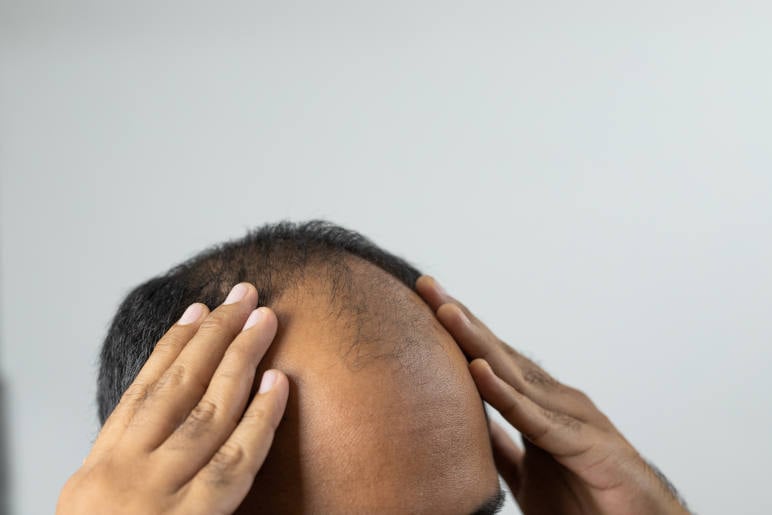
Types of alopecia: causes, treatments and more
Alopecia refers to the partial or complete absence of hair from areas where it normally grows, and about 2% of people across the world will experience this form of hair loss at some point in their lifetime.
For individuals with alopecia, predicting the pattern of hair loss, regrowth, severity, and duration proves challenging. That said, there are some common symptoms of alopecia and hair loss that are good to know and recognise.
Learn about the main types of alopecia: androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, sudden hair loss and traction alopecia, as well as how to tackle them effectively.
Summary
- What Is Alopecia?
- What Are the Different Types of Alopecia?
- Androgenetic Alopecia
- Alopecia Areata
- Traction Alopecia
- Sudden Hair Loss
- What Are the Treatments for Sudden Hair Loss?
- How We Can Help With Alopecia?
What Is Alopecia?
Alopecia is a medical condition characterised by partial or complete hair loss, often resulting from autoimmune disorders, genetic hormonal changes, or other underlying health issues. It can affect any part of the body where hair grows, including the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
Alopecia can have various forms, such as alopecia areata (patchy hair loss), alopecia totalis (complete loss of scalp hair), or alopecia universalis (total loss of body hair).
It can also impact people at any age in both men and women, although it’s known to be more common among males.
What Are the Different Types of Alopecia?
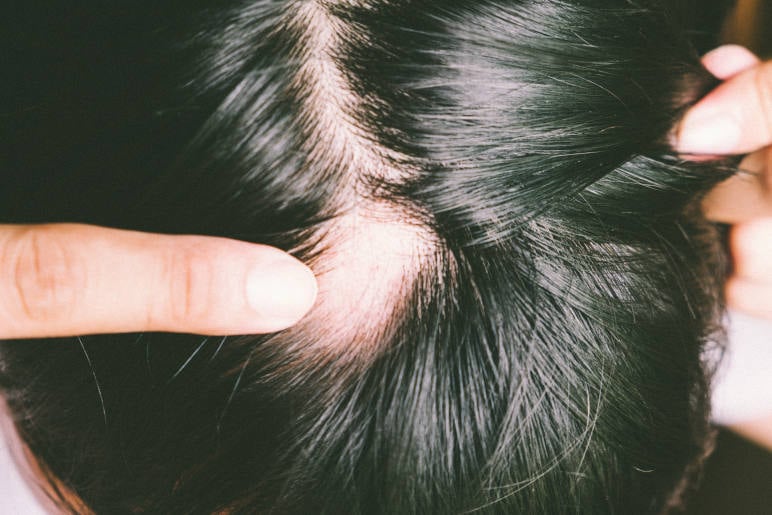
There are a number of different types of alopecia that range from mild, to more severe hair loss. These include:
- Alopecia areata
- Traction alopecia
- Sudden hair loss: Telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium
- Alopecia Totalis
- Alopecia Universalis
- Alopecia Barbae
- Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)
- Cicatricial alopecia
There are, however, three that stand out as the most common among individuals around the world, which are androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, traction alopecia, as well as sudden hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is a genetically predetermined condition caused by an excessive response to androgens. It affects around 50% of both men and women, leading to gradual hair loss on the scalp after puberty.
Hair loss in males typically occurs at the vertex and frontotemporal regions, whereas females often maintain their frontal hairline but experience diffuse thinning at the crown, resulting in a wider appearance at the front of the hair.
What causes androgenetic alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia is primarily caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors:
- Genetic predisposition, inherited from both parents.
- Hormonal influences, particularly the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which shrinks hair follicles.
- Ageing, which increases the sensitivity of follicles to DHT, resulting in progressive hair thinning and loss.
Treatments for androgenetic alopecia
Treatments for androgenetic alopecia include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Topical medication applied to the scalp to promote hair growth.
- Finasteride (Propecia): Oral medication that blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT.
- Low-level laser therapy (LLLT): Stimulates hair follicles to promote growth.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Involves injecting plasma-rich platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
- Hair transplant: Surgical procedure to transplant hair follicles from donor areas to balding regions on the scalp.
Suitable for a hair transplant?
Yes, hair transplants are an effective treatment for androgenetic alopecia. During the procedure, healthy hair follicles from donor areas are transplanted to balding or thinning areas on the scalp. This restores natural hair growth and density, providing long-lasting results for individuals experiencing pattern baldness. If you are struggling with treating your androgenetic alopecia, book a free consultation today with our specialists.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other parts of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Symptoms of alopecia areata loss include patchy hair loss, which can happen very suddenly. The hair follicles can become inflamed, causing an itching or burning sensation, but this usually resolves on its own.
What causes alopecia areata?
Studies have shown that genetics play a key role in alopecia areata, with one in every five people who had the condition also having a family member who suffered from it. That said, it can also be attributed to:
- An autoimmune reaction, where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- Certain environmental factors like stress, illness, or trauma can trigger or exacerbate the condition.
- Abnormalities in the immune system, such as overactivity or dysregulation, may also play a role in the development of alopecia areata.
Treatments for alopecia areata
Treatments for alopecia areata include:
- Medications: Minoxidil and finasteride can slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Stimulates hair growth by injecting platelet-rich plasma into the scalp.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Activates hair follicles to encourage growth.
- Topical solutions: Some contain ketoconazole or caffeine to improve hair density and thickness.
Suitable for a hair transplant?
Hair transplants are generally not recommended for alopecia areata because it’s an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles. However, in certain cases where the condition has stabilised and there are areas of permanent hair loss, a hair transplant may be considered. It’s important to consult with a specialist to determine the suitability of a hair transplant and to explore other treatment options first.
Traction Alopecia
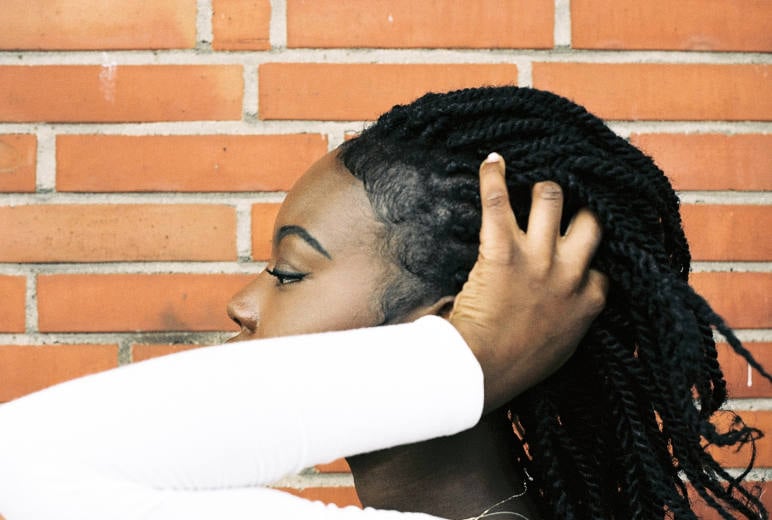

Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss caused by prolonged or repetitive tension on the hair follicles, often due to hairstyles that pull tightly on the hair. The constant pulling can damage the hair follicles, leading to gradual hair thinning or bald patches, particularly along the hairline or in areas where tension is applied.
What causes traction alopecia?
The causes of traction alopecia can be attributed to:
- Tight hairstyles such as ponytails, braids, or cornrows.
- Prolonged use of hair extensions, wigs or weaves that tug on the hair follicles can contribute to traction alopecia.
- Constant use of hair accessories like hairbands or clips that pull on the hair can lead to traction alopecia.
Treatments for traction alopecia
The treatments for traction alopecia include:
- Changing hairstyle: can help to reverse this type of hair loss.
- Supplements including biotin: can help with hair health and growth
- Boost hair growth naturally: using a healthy, varied diet and hair treatments
- Hair transplant surgery: may be necessary in severe cases to replace the lost hairs.
Suitable for a hair transplant?
If you’ve had no visible regrowth from treatments after three months and it seems the hair follicles are dead, individual cases should first be assessed by one of our specialists and rule out alopecia due to other reasons. A permanent solution is a hair transplant using the DHI technique.
Sudden Hair Loss
Sudden hair loss refers to a rapid and unexpected shedding of hair within a short period. Conditions such as telogen effluvium and anagen effluvium are common causes of sudden hair loss and can manifest as thinning of the hair, bald patches, or excessive shedding during brushing or washing.
What causes sudden hair loss?
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen Effluvium is characterised by a sudden shedding of hair caused by a disruption in the hair growth cycle, often triggered by stress, illness, hormonal changes, or nutritional deficiencies. This condition leads to a larger number of hair follicles entering the resting phase simultaneously, resulting in noticeable hair loss after a few months.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen Effluvium, on the other hand, is typically caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy, resulting in the abrupt cessation of hair growth as hair follicles are damaged during the active growth phase.
What Are the Treatments for Sudden Hair Loss?
Telogen Effluvium
The hair often grows back on its own, but some telogen effluvium treatments can be used to aid in hair growth:
- Topical solutions: can help to bridge the gap between hair loss and regrowth.
- Addressing nutrient deficiencies: can be detected by seeking medical advice with a blood test.
- Reducing stress: can help with producing hair if it is the cause.
Anagen Effluvium
The hair will also often grow back, but to speed up the process, patients are recommended:
- Topical solutions: can help with hair regrowth
- Scalp cooling: used during chemotherapy, it can help to reduce or prevent dramatic hair loss.
Suitable for a hair transplant?
Hair transplants are generally not recommended for Telogen Effluvium and Anagen Effluvium. These conditions involve temporary disruptions in the hair growth cycle, and the hair usually regrows naturally once the underlying cause is addressed. Hair transplant procedures are more suitable for permanent hair loss conditions where the hair follicles are permanently damaged or absent.
How We Can Help With Alopecia?
At Elithair, our team of experts specialises in addressing various forms of alopecia, providing comprehensive consultations to determine the most effective approach for hair regrowth.
Don't let alopecia hold you back any longer: schedule your consultation now for personalised solutions and expert guidance.
FAQ
How can diet impact alopecia and hair loss?
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially iron, zinc, and biotin, can help support hair health and may reduce the risk of hair loss associated with nutrient deficiencies.
Can stress management techniques help with alopecia?
Yes, managing stress through techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help reduce the impact of stress-related hair loss and support overall hair health.
Are there any preventive measures for alopecia?
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding tight hairstyles, managing stress, and using gentle hair care practices to minimise hair follicle damage.
What are the latest advancements in alopecia treatment?
Recent advancements include the use of JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata, stem cell therapy, and more effective formulations of PRP therapy, offering promising results for hair regrowth.
How do I know if my hair loss is temporary or permanent?
A thorough evaluation by a hair loss specialist, including medical history, physical examination, and possibly scalp biopsy or blood tests, can help determine if hair loss is temporary or permanent.