ow Does Hair Grow? The Hair Growth Cycle, Speed & What Affects It (UK 2026 Guide)
For many of us, our hair is a central part of our identity. Especially as part of how we present ourselves to the wider world. As we age our hair growth and health changes in accordance with our lifestyle or as part of our genetics. Sometimes it isn’t in the health we’d like it to be in.
So in order to improve the condition of our hair, we need to understand; how does hair grow?
- How Does a Hair Strand Form and Grow?
- What Are the Stages of Hair Growth?
- How Fast Does Scalp Hair Grow?
- What Affects Hair Growth—and What Causes It to Slow or Stop?
- Can I Make My Hair Grow Faster?
- Is it Possible to Grow Hair Back?
- Evidence-Based Ways to Support Healthy Hair Growth
- When Hair Growth Stops—or Seems to Stop—What Should You Do?
- Conclusion
- FAQ
How Does a Hair Strand Form and Grow?
Hair strands grow from the root of the hair follicle. Formed by cells multiplying and fed by blood vessels in your scalp, hairs are then pushed up through your skin as it grows.
As the hair follicle moves up through your scalp, it produces a hard protein called Keratin. This is a protective protein you find in your skin, hair, and nails. As it forms Keratin gathers oils from surrounding glands to keep your hair shiny and soft.
Finally, once your hair has reached the top of the hair shaft it emerges from your skin. At this stage it is no longer ‘living’ as it is external to the body. You may be wondering “how does hair grow if it’s dead?”
Although it’s dead after leaving the surface of the skin, the follicle and root are still alive, which continues the transformation of keratin into hair growth.
What Are the Stages of Hair Growth?
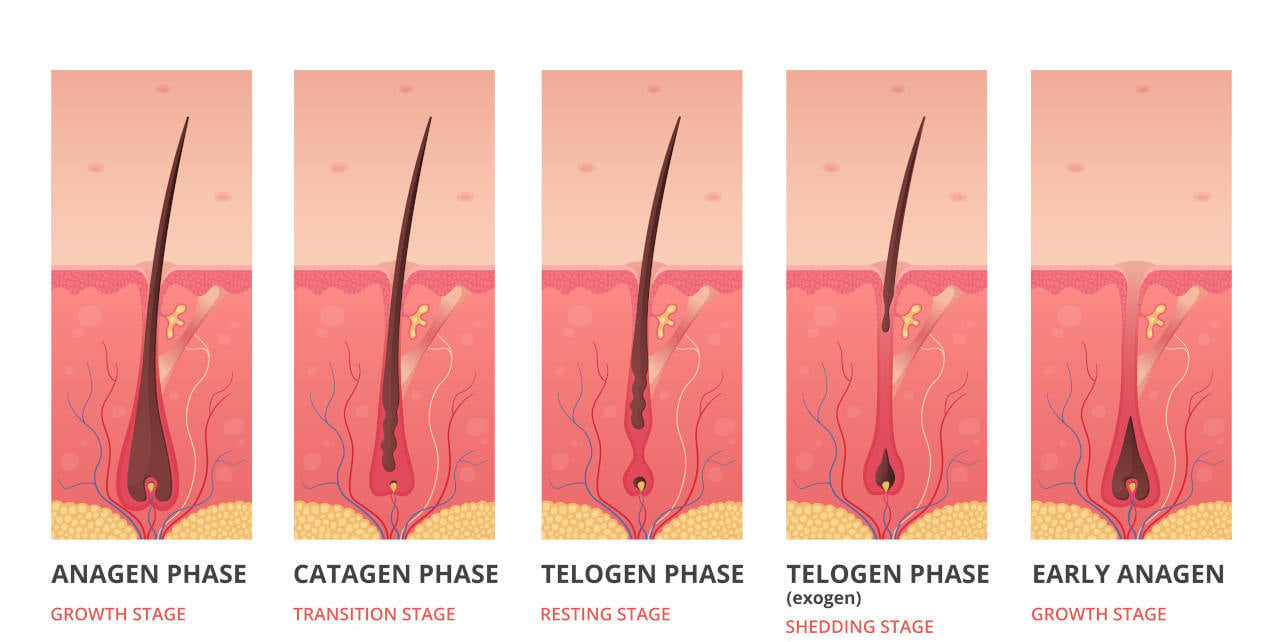
Your hair grows from a tiny organ called the hair follicle, which ushers each strand through four distinct phases:
| Phase | Name | What Happens | Typical Duration* |
| Growth | Anagen | Matrix cells divide and push the hair shaft outward. The follicle is active and deep in the dermis. | 2-8 years (scalp) |
| Transition | Catagen | Follicle shrinks and growth stops; the lower part regresses. | ~2-3 weeks |
| Resting | Telogen | Hair no longer grows; follicle stays inactive before shedding. | ~2-4 months |
| Shedding | Exogen | The old hair is released and new anagen begins; sometimes included as part of telogen. | ~Variable |
*Durations vary between individuals and with age, health and hair type. On the scalp, about 80-90 % of follicles are in anagen at any one time.
What this means is that at any moment you’re shedding some hairs while new ones grow. Losing 50-100 hairs per day is considered normal.
How Fast Does Scalp Hair Grow?
- On average, scalp hair grows at around 0.3-0.4 mm/day, which is roughly 1 to 1.2 cm per month (≈12-15 cm/year) for many people. [
- Growth slows down with age because the anagen phase tends to shorten and shaft thickness can drop.
- Your personal growth rate is influenced by genetics (how long your follicles remain in anagen), health, scalp blood flow and the absence of external damage.
Important: While you can support healthy growth, you cannot significantly accelerate growth beyond your genetic-biologic limit.
How to grow hair faster
Specific products and ingredients can allow for improved hair growth. Caffeine is an excellent example of a growth promoting product.
Caffeine also counteracts DHT Dihydrotestosterone, a hormone that is known for rapid and early onset hair loss. Moreover, caffeine stimulates the blood supply to your scalp, which is a crucial step for hair growth. Caffeine enriched shampoos have been known to help grow hair faster.
What Affects Hair Growth—and What Causes It to Slow or Stop?
There are several types of alopecia that can make your hair stop growing. The 5 main reasons for those are:
Genetic and Hormonal Influences
The most common reason hair growth slows or becomes thin is androgenetic alopecia (AGA) — a hereditary condition where hair follicles shrink (miniaturise) over time due to sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
In AGA the anagen phase shortens, telogen becomes frequent, and follicles may eventually stop producing visible hair entirely.
Nutrition, Health & Lifestyle
Hair matrix cells divide rapidly and require nutrients to maintain normal growth. Deficiencies in iron, zinc, protein, vitamin D or B-vitamins may impair hair growth or lead to increased shedding (telogen effluvium).
However: in most healthy people with a balanced diet, nutrient status is only one piece of the puzzle.
Stress, Illness & Life Events
Major physical or emotional stress, illness, surgery or crash dieting can shift many hairs into telogen—leading to noticeable shedding around 2–3 months later. This is temporary if the trigger is removed.
Chronic stress may also exacerbate pattern hair loss by influencing hormones, inflammation and scalp follicles.
Scalp & Follicle Environment
- Poor circulation, chronic inflammation (seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis), or scarring can damage follicles.
- External damage: Excessive heat, chemical treatments, tight hairstyles (traction alopecia) weaken shafts and may damage follicles.
- Smoking, poor sleep, high sugar diet and alcohol may impair scalp health indirectly.
Age and Follicle Reserve
With ageing, many follicles gradually shrink, anagen phases shorten and growth slows. By middle age many people notice reduced hair-density and slower growth. Recognising early signs is key.
Can I Make My Hair Grow Faster?
Short answer: not significantly beyond your biological limit. Many products claim to “speed up growth”, but strong evidence is lacking. Ingredients like caffeine in shampoos show minor benefits in small studies (e.g., increased shaft length or density), but they cannot override genetics or restore lost follicles.
The most effective route to thicker, fuller hair when follicles are miniaturising is early diagnosis and treatment (medical or surgical) rather than purely trying to “grow hair faster”.
Is it Possible to Grow Hair Back?
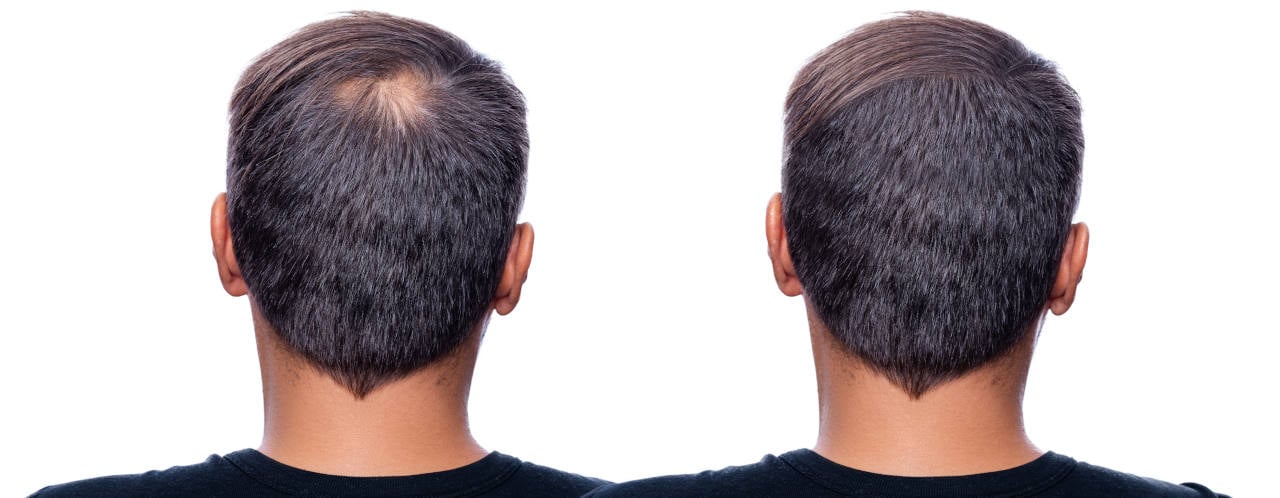
If you’ve lost some hair (depending on how much you’ve lost and your hair health) you can get medication from a specialist to reactivate your dormant skin follicles. However, if a follicle is damaged, closed or hasn’t generated hair in years, it will unfortunately not grow back.
In this case, a hair transplant using your remaining hair would be a permanent option, in order for you to restore a full head of hair.
Evidence-Based Ways to Support Healthy Hair Growth
Here are practical steps you can take — remember: they support existing follicles, but cannot resurrect those that are permanently lost.
- Ensure a balanced diet: Adequate protein, iron, zinc, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids support hair-matrix cell division.
- Avoid extreme diets and rapid weight-loss: These triggers shedding.
- Limit heat and chemical damage: Use lower-heat styling, reduce bleaching, avoid very tight hairstyles.
- Maintain scalp health: Clean, well-circulated scalp supports follicle function. If you have dandruff/itching, seek dermatologist input.
- Manage stress and sleep: Good sleep and stress-management help overall hair-cycle stability.
Seek early evaluation: If you notice thinning, receding hairline or increased shedding, early medical intervention improves outcomes.
When Hair Growth Stops—or Seems to Stop—What Should You Do?
It’s time to seek a specialist if you notice:
- Sudden patchy hair-loss or scarring (possible alopecia areata or scarring alopecia)
- Shedding >150 hairs per day, or shedding lasting over 6 months
- Receding hairline or thinning crown in your 20s/30s (possible pattern hair loss)
- Itching, pain, inflammation, visible scalp or red patches
- Underlying medical conditions (thyroid disease, iron deficiency, medications)
A hair-loss specialist will assess your scalp (dermoscopy/trichoscopy), check your history, run blood tests, and recommend an evidence-based treatment plan suited to you.
Conclusion
If you think your hair has stopped growing, noticed your hair thinning or less and less hair regrowth, take a look at your scalp and seek medical advice from a registered specialist.
Furthermore, Dr Balwi at Elithair advises patients on the best course of action for hair care, hair treatments and hair transplants at our clinic in Turkey and speaks internationally on hair transplant techniques.
Do you have any more questions or are you suffering from hair loss issues? Then feel free to to contact our friendly team who are on hand to answer all your queries.
FAQ
How does the environment impact hair growth?
Environmental factors like pollution, UV radiation, and harsh weather conditions can damage hair follicles and affect hair growth. Protecting hair from these elements can help maintain healthy growth.
What role do hormones play in hair growth?
Hormones like androgens significantly influence hair growth. Imbalances can lead to conditions such as androgenetic alopecia, where hair follicles shrink and hair growth slows down.
Can certain medications impact hair growth?
Yes, medications such as chemotherapy drugs, beta-blockers, and some antidepressants can impact hair growth, often leading to temporary or permanent hair loss. Regarding the latter, below is a list of antidepressant drugs that can cause hair loss:
-
Zoloft (sertraline)
-
Prozac (fluoxetine)
-
Janimine (imipramine)
-
Anafranil (clomipramine)
-
Paxil (paroxetine)
-
Tofranil (imipramine)
-
Adapin (doxepin)
-
Sinequan (doxepin)
-
Surmontil (trimipramine)
-
Pamelor (nortriptyline)
-
Ventyl (nortriptyline)
-
Norpramin (desipramine)
-
Elavil (amitriptyline)
-
Haldol (haloperidol)
-
Asendin (amoxapine)
-
Endep (amitriptyline)
-
Pertofrane (desipramine)
-
Vivactil (protriptyline hydrochloride)
Are there any specific vitamins or supplements that can promote hair growth?
Vitamins such as biotin, vitamin D, and iron are crucial for hair health. Supplements containing these vitamins can support hair growth and strength, but those should always be taken as a complement to a balanced diet.
How do hair care practices influence hair growth?
Proper hair care, including regular washing, conditioning, and avoiding excessive heat styling, can protect hair follicles and support healthy growth.
Is it normal to lose 100 hairs a day?
Yes. Most people lose 50–100 hairs daily as part of the normal cycle because some follicles are in the telogen/shedding phase at any time.
Will my hair keep growing longer if I leave it untrimmed?
Not indefinitely. Hair stops growing when its anagen phase ends; genetics determine how long it can grow.
My hair has stopped growing in a patch — can it grow back?
If the follicle is still active but in telogen or miniaturised, yes. If the follicle is destroyed or scarred, regrowth may not occur without medical/surgical intervention.
When should I see a specialist?
If you notice thinning, receding hairline or increased shedding, especially at young age, or if you have signs of scalp disease. Early review gives better chances of preserving hair.