What Is the Difference Between Fut and Fue Hair Transplants?
Although there are various hair transplant techniques that exist, the two most common types of hair transplant performed today are Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). Both techniques have been developed over decades of research and procedures, and there are some important distinctions between the two approaches.
In this article, we’ll be explaining both techniques in detail and highlighting the key differences between them, giving you everything you need to know in order to make an informed decision on your hair transplantation surgery.
What Is Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)?
Regardless of technique, the back of the head is always used as a “donor area” in hair transplants. This is because the hair which grows in this area is DHT resistant, meaning it is not prone to shedding and remains abundant and healthy, even when balding occurs elsewhere on the scalp.
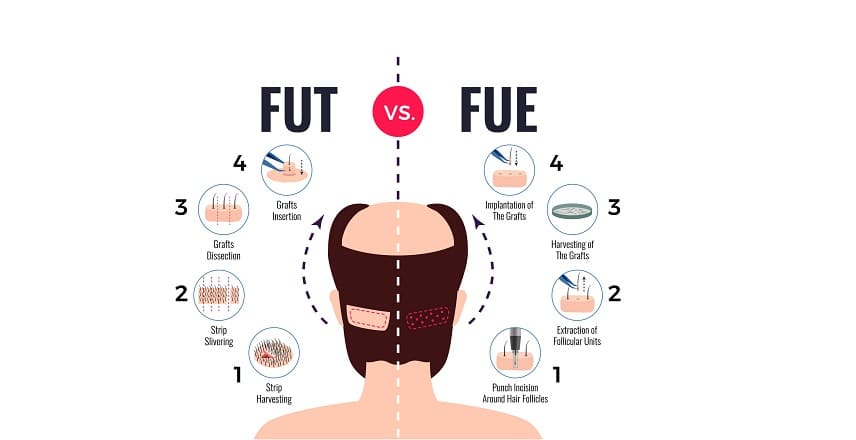
The FUT hair transplant, also known as the “strip” method, involves removing a strip of scalp from the back of the patient’s head. This section of scalp is comprised of hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and nerves. The extracted strip is then dissected into separate follicular units containing 1-4 hairs under a microscope, whereupon the follicles are implanted into the patient’s scalp in the areas affected by balding.
Due to the invasive nature of the procedure, local anaesthesia is used as part of the FUT hair transplant process. The donor area is sutured by the surgeon, which eventually leaves a long horizontal scar at the back of the head. Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the entire procedure can take 3-8 hours.
What Is Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)?
In the case of Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), hair grafts are harvested individually from the donor site, eliminating the need to extract a strip of scalp and divide the extracted tissue under a microscope. To do this, the surgical team uses a thin, hollow needle that can be operated manually or with a micromotor. Once the grafts are extracted, they are placed in a biotin-rich solution to keep the follicles strong and healthy before they are implanted into the balding areas of the scalp.
The FUE method was developed specifically to address and improve upon the shortcomings of the FUT technique. It is considered a more advanced procedure with greater benefits for the patient. For instance, the recovery time from FUE is significantly lower than that of FUT, and involves next-to-no scarring. However, the FUE technique can often take longer than FUT as it is a more complex procedure and requires more precision.
When receiving an FUE procedure at Elithair, you will be given a NEO FUE hair serum preparation. This Elithair exclusive product primes your scalp for the surgery, significantly increasing growth rate and hair density following your procedure.
What Are the Main Differences Between FUE and FUT Hair Transplants?
- Recovery Time: As FUE is a far less invasive procedure than FUT, patients typically recover much faster and can return to their daily lives sooner, often within 3-5 days.
- Scarring: FUT invariably causes a noticeable horizontal scar at the back of the head. FUE, by contrast, requires no incisions, only small punches with a needle. While the puncture sites do experience some scarring, these scars are so small that they are often concealed by the patient’s hair.
- Numbing: Scalp numbness is a common side effect among FUT patients, as nerve tissue is severed when extracting the skin. This can take up to six months to improve. Meanwhile, any residual numbing experienced by FUE patients tends to resolve sooner.
- Size: FUE is commonly considered a better choice for smaller transplants. Contrary to what many believe, total hair loss is not common, and many patients only require a partial transplant – especially if they are under the age of 35.
- Recovery: While all patients of hair transplants are prohibited from strenuous exercise for at least two weeks following surgery, FUE patients find that they can return to their usual routines sooner, thanks to the ease with which the puncture wounds recover compared to the stitched incision of an FUT procedure.
- Discomfort: As FUE is far less invasive than FUT, patients report less pain and discomfort following the operation.
- Versatility: While FUT is only recommended for use in the transplantation of hair to the scalp, FUE can be used for extracting follicles to be implanted into the beard and even eyebrows.
- Scalp Tension: The skin on the scalp is often quite tight, with little elasticity compared to other areas of the body. Due to this tension, FUT is not always possible, as the skin would not have enough “give” to allow for closing the incision. This, however, is not a concern for FUE, which can be performed on both loose or tight scalps.
Success Rates of FUT and FUE Hair Transplants
Both FUT and FUE techniques can provide excellent results when performed properly by trained professionals. It is difficult to determine an accurate FUT vs FUE success rate, as each individual case is different and there are multiple variables at play. However, studies show that FUE can yield exceptional results in skilled hands, with the “two most important factors in success of FUE [being] accuracy and speed which come with time and practice.”
Studies from Tsilosani found survival of the FUE grafts equivalent to that of FUT grafts. Here at Elithair we have found consistent patient satisfaction in our hair transplants.
Which Hair Transplant Is Best for Me?
When choosing how to approach your hair restoration, FUT and FUE are the most common and effective methods of extraction. While FUT is still widely performed as a technique, these days it is considered less safe than alternatives and is followed by a longer recovery period.
While the FUE procedure itself may be lengthy, we prioritise the safety and outcome of our patients, which is why this is the technique in which we specialise at Elithair. For a complete overview of what to expect before, during, and after the procedure, read our guide to hair transplants in Turkey.
We hope that this article has given you the information necessary for making a sound decision if you are considering a hair transplant. If you have any questions about thinning hair or wish to receive a free hair analysis, simply contact our consultants. We will be happy to assist you with any enquiry regarding FUE hair transplants and discuss the best options for you.
FAQ
What are the cost differences between FUE and FUT procedures?
Generally, FUE tends to be more expensive than FUT due to its complexity and the time required for the procedure. The exact cost can vary based on the number of grafts and the clinic’s pricing structure.
Which method has a higher graft survival rate?
Both FUE and FUT have high graft survival rates when performed by experienced surgeons. However, FUE may have a slightly higher survival rate due to the less invasive extraction process.
What are the potential long-term complications of each method?
FUT can result in a linear scar and potential numbness at the donor site. FUE may cause tiny dot scars, but typically has fewer long-term complications. Both methods can have risks of infection and folliculitis if not properly managed.
How do I decide which method is best for my specific hair loss pattern?
A consultation with a hair transplant specialist can help determine the best method based on your hair loss pattern, scalp laxity, and personal preferences for scarring and recovery time.
Are there any differences in the post-operative care for FUE and FUT?
Post-operative care for both methods includes keeping the scalp clean, avoiding strenuous activities, and following medication guidelines. FUT may require more care due to the linear incision.