The Hair Growth Cycle: Understanding How Hair Grows
How can you distinguish between natural hair shedding and unusual hair loss? Understanding the hair growth cycle offers valuable insights. This cycle governs the growth of your hair and body hair through a specific pattern.
In this article, we’ll explore each stage of the cycle, explain the differences between hair and body hair, and highlight four key factors that can disrupt the cycle.
The Hair Growth Cycle: 3 Phases
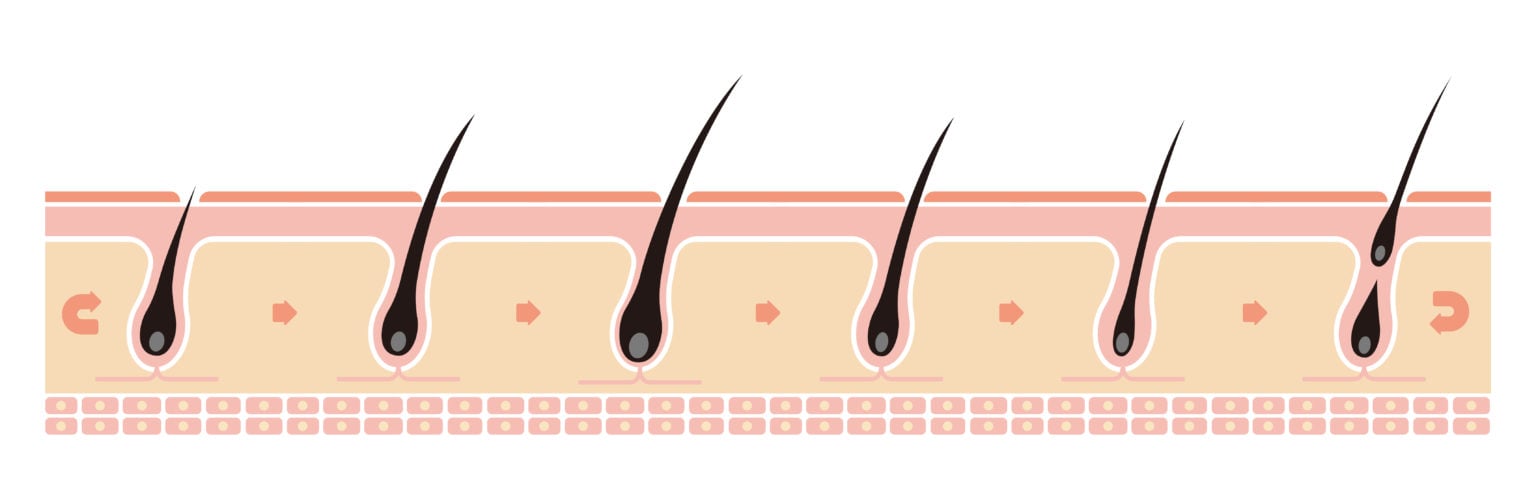
The hair growth cycle consists of three stages: anagen, catagen, and telogen. This process repeats 25 to 30 times throughout our lives. Let’s delve into each phase:
Anagen Phase
This is the growth phase, where the hair actively grows. It is the longest phase, lasting between 3 and 6 years.
Hair follicles, located beneath the scalp, produce keratinocytes—cells that form the hair shaft. These cells divide rapidly and die, stacking up to push older cells to the surface, creating the visible strand of hair.
Catagen Phase
Known as the transition phase, this stage lasts 2 to 3 weeks. Hair stops growing and begins detaching from its follicle. The root moves closer to the skin’s surface as the hair gradually ceases its activity.
Telogen Phase
The final phase, also called the resting phase, occurs when the hair follicle and cells are dormant. The hair stops growing but does not fall out immediately.
Hair shedding happens when a new strand begins its anagen phase, pushing out the old hair. This stage lasts around 2 to 3 months before the cycle restarts with new growth.
Hair, Beards, Eyebrows: Different Growth Cycles
Hair and body hair are composed of the same material, but their growth cycles differ based on their location. Here’s a comparison:
| Type | % in Anagen Phase | % in Telogen Phase | Telogen Duration | Density/cm² | Follicle Depth |
| Hair | 80–90% | 10–20% | 3–4 months | 350 | 3–5 mm |
| Beard | 70% | 30% | 10 weeks | 500 | 2–4 mm |
| Eyebrows | 10–15% | 85–90% | 3 months | 50 | 2–2.5 mm |
4 Factors That Influence the Hair Growth Cycle

Genetics
Some individuals inherit a predisposition to shorter and fewer cycles, particularly in cases of androgenetic alopecia (hereditary hair loss). Sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can accelerate the cycle, leading to premature hair loss.
Hormones
Oestrogens can extend the anagen phase, while androgens and thyroid hormones tend to shorten it, potentially affecting growth.
Nutrition

Your diet has a direct impact on hair quality. Proteins, zinc, iron, and B vitamins are essential nutrients for healthy growth.
Seasons
Environmental changes such as temperature, light, and humidity can influence hair shedding. Spring and autumn are typically when shedding is most noticeable.
When the Cycle Goes Off Track
The hair growth cycle naturally evolves with age. During childhood, the body produces more anagen phases, while after 50, the cycle tends to shorten.
Regular monitoring of your hair’s health can help identify unusual hair loss patterns early. For men, consulting a specialist can lead to timely intervention, whether through medication or advanced treatments like hair transplantation.
For women, hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or menopause, can significantly affect hair growth and shedding.
If you’re concerned about hair loss or are considering a hair transplant in Turkey, contact our experts today for your free hair analysis.
FAQs
What environmental factors affect the hair growth cycle?
Pollution, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can disrupt hair growth and health.
How do medical treatments impact hair cycles?
Medications, such as those for cancer treatment, can interfere with the cycle, causing temporary or permanent hair loss.
How does age influence the hair growth cycle?
The anagen phase shortens with age, leading to slower, thinner regrowth.
What are signs of abnormal disruptions in the cycle?
Excessive shedding, bald patches, or overall thinning can indicate cycle irregularities
How can nutrition support a healthy hair cycle?
A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins (A, B, C, D, E), and minerals like zinc and iron is vital for hair health.
What role does stress play in hair loss?
Stress can trigger an acceleration of the telogen phase, increasing shedding.
What treatments can restore a disrupted cycle?
Options include topical medications like minoxidil, PRP therapy, or hair transplants. Always consult a doctor for personalised advice.
How do eyebrow and eyelash cycles differ from scalp hair?
Their cycles are shorter, with fewer hairs in the anagen phase and more in the telogen phase.
What are the effects of seasonal changes on the hair cycle?
Seasonal variations can influence the rate of hair loss, especially in Spring and Autumn.
What are the signs of hereditary baldness in the hair cycle?
A gradual shortening of growth phases and miniaturization of hair follicles are signs of hereditary baldness.