Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia): Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment & Prognosis (UK 2026 Guide)
When you have hair loss the first thing you want to know is how to get your hair back quickly. Well, the first thing that you need to do is to identify what is causing your hair to fall out. From the diagnosis, you will know whether you have Non-Scarring or Scarring Alopecia.
The treatment options for both categories of alopecia are very different, which is why you need to know the cause first. We take a closer look at this below.
Non-Scarring v.s Scarring Alopecia
To identify whether you have Scarring Alopecia (SA) or Non-Scarring Alopecia you need to consult your doctor or dermatologist. They will conduct a hair pull test and possibly a scalp biopsy to assess whether your hair follicles are still alive and for the presence of inflammatory cells.
What is Scarring Alopecia?
Scarring alopecia is permanent damage caused to the hair follicles which is replaced with scar tissue. Scar tissue completely destroys the hair bulb thus ceasing the hair growth cycle forever.
The science behind this is that when inflammation occurs around the hair follicles, the stem cells and oil glands (sebaceous glands) at the top of the bulbs are destroyed. Without these, hairs cannot grow and are permanently lost.
What is Non-Scarring Alopecia?
Non-Scarring Alopecia is the reversible kind of hair loss whereby the hair follicles are still alive and hair growth can return. In some cases, the hair fall and regrowth occur for unknown reasons and it’s difficult to predict the duration of the hair fall.
On the other hand, some patients experience cycles of hair loss and hair regrowth that is unpredictable. However, there is always a chance of new hair appearing which isn’t the case with SA.
Which types of alopecia are scarring and non-scarring?
Those do not refer to just one type of alopecia. Each form of hair loss is identified as either the former or the latter. Here is a definition of which alopecia conditions are in which category:
Non-Scarring Alopecias:
- Alopecia Areata
- Alopecia Areata Totalis
- Short-term Traction Alopecia
- Alopecia Areata Universalis
- Alopecia Barbae
Scarring Alopecias:
- Lichen Planopilaris
- Cicatricial Alopecia
- Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia
- Long-term Traction Alopecia
- Hair loss due to injury (surgical scars)
Some hair loss conditions cause severe itching, burning, and scalp discomfort that indicates that your hair is affected by something. When these symptoms occur, you need to seek advice from your doctor or dermatologist.
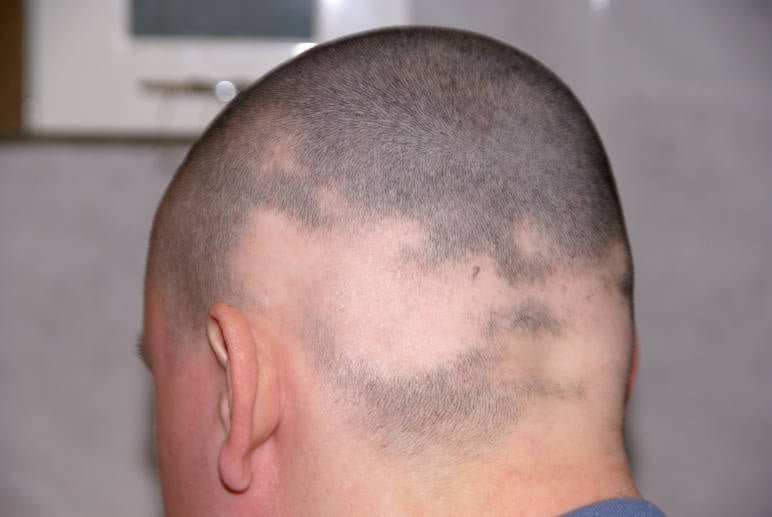
What Does Scarring Alopecia Look Like?
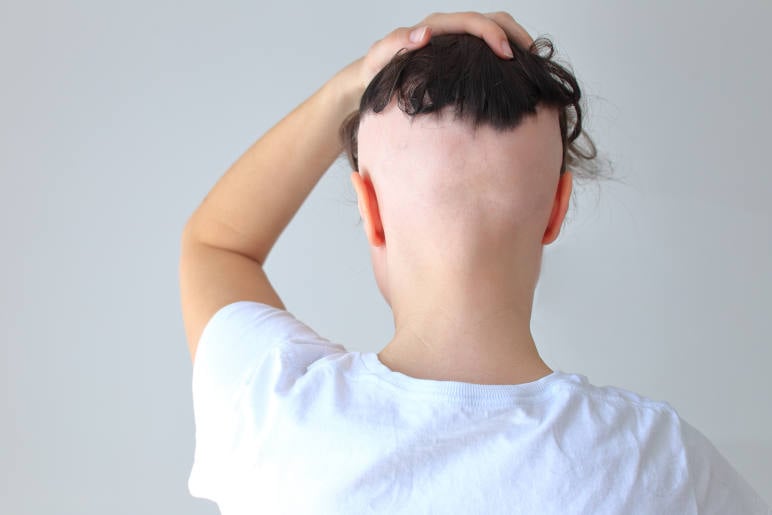

This form of hair loss looks like scarred skin surface where your hair used to be. The surface of the skin will look less or more pigmented, shiny, and smooth. And of course completely bald.
Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia is a good example. It’s caused by Lichen Planopilaris which progressively destroy the hair follicle from the frontal hairline and works its way backwards.
Alopecia Areata, which is a patchy form of hair loss is often confused with scaring alopecia because of the smooth patches it creates. However, AA is actually a type of non-scarring hair loss as the hair growth can return naturally.
Can Hair Grow Back Afterwards?
If scarring alopecia is identified early then it is possible to treat the inflammation to stop or at least slow down the progression of your hair loss. To treat the inflammation, anti-inflammatory medication (usually a topical treatment) is prescribed such as:
- Antibiotics
- Corticosteroids
- Immunotherapy (when an autoimmune disease is a cause e.g. thyroid disease)
Although these medications can be effective, they are not effective in every case, especially when the diagnosis is unknown. Hence, it’s important to get a proper diagnosis early on in order to reduce the effects of inflammation.
Can Scarring Alopecia Be Treated?
A hair transplant is an excellent treatment for Scarring Alopecia because alive, growing hairs are implanted into the scar tissue. This restores the hair that was there before, thus returning your full head of hair. For a complete overview of the procedure, recovery process, and pricing options available abroad, read our guide to hair transplants in Turkey.
However, in order for a hair transplant to be successful, you need sufficient donor hair grafts. Also, the cause of your hair loss needs to have settled before a hair transplant is possible.
Treatment Goals & Realistic Expectations
- Primary aim: suppress inflammation, stabilise disease, preserve remaining follicles.
- Secondary aim: regrow hair where possible—but significant regrowth is less likely once follicles are destroyed.
Cosmetic alternatives: if follicles are lost, options include wigs, scalp micropigmentation, hair transplant only if disease is inactive.
What Treatments are Used?
| Treatment | Use & evidence | Notes / limitations |
| Topical/intralesional corticosteroids | First-line for many lymphocytic forms. | Works mainly if inflammation is active and follicles intact. |
| Oral agents (e.g., hydroxychloroquine, doxycycline, isotretinoin) | For immune/inflammatory forms (LPP, FFA, CCCA) | Off-label, many without large RCTs; side-effects must be managed. |
| Low-level light therapy/other adjuncts | Emerging evidence in some subsets. | Still experimental; not universally available. |
| Hair transplant/grafting | Considered only when disease is quiescent; many forms unsuitable. | Must be done by experienced specialist; outcomes variable. |
Conclusion
When it comes to hair loss, time is usually against you. Although this seems like a very frightful statement, it means that you have a better chance of keeping your hair if you act sooner rather than later.
This is especially relevant for progressive forms of hair loss, and definitely types that are caused by inflammation. The sooner the inflammation is reduced, the less scaring alopecia you will have. Thus, it will be more naturally reversible.
FAQ
Can scarring alopecia be mistaken for other types of hair loss?
Yes, scarring alopecia can be mistaken for other types like alopecia areata due to similar initial symptoms. A proper diagnosis often requires a scalp biopsy.
What are the early symptoms of scarring alopecia?
Early symptoms include itching, burning, and redness around hair follicles, followed by gradual hair thinning and the appearance of bald patches with a shiny or scarred surface.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage scarring alopecia?
Managing stress, avoiding harsh hair treatments, and using gentle hair care products can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage.
How effective are hair transplants for scarring alopecia?
Hair transplants can be effective if there is enough donor hair and the inflammation causing the alopecia is under control. Success depends on individual cases and severity.
Can scarring alopecia lead to permanent hair loss?
Yes, scarring alopecia causes permanent hair loss due to the destruction of hair follicles replaced by scar tissue. Early treatment can help manage symptoms and slow progression.
Is scarring alopecia curable?
Not in the sense of full follicle regeneration once scar tissue forms. The goal is disease stabilisation and preserving remaining hair.
How is it different from pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia)?
Pattern baldness is non-scarring—hair follicles miniaturise but remain intact, so partial regrowth is possible. Scarring alopecia destroys follicles and replaces them with scar tissue, making regrowth much less likely.
Can I have a hair transplant if I have scarring alopecia?
Possibly—but only after the inflammation is fully inactive (usually >12–24 months) and you must be assessed by an experienced surgeon. Some forms are unsuitable entirely.
My scalp itches and has red patches—could this be scarring alopecia?
Yes. Scalp symptoms like itching, burning, redness plus new bald patches are warning signs. Get a specialist assessment.
Will changing hairstyle or avoiding tight styles help?
In secondary forms that arise from trauma/styling yes, reducing trauma may prevent further damage. But if the condition is already active or primary inflammatory type, further specialist treatment is required.